Finishing Services
If you need your parts produced with Xometry to be further post-processed, you can indicate it in the Instant Quoting Engine and choose from 40+ finishing options in just a few clicks.
Xometry will work with you from design to production, right through to the finishing of your parts to achieve the required surface finish and functionality.
Quote Your Parts With One of 40+ Finishes
to improve the surface and the aesthetic and functional properties of your parts
Surface Treatments
-
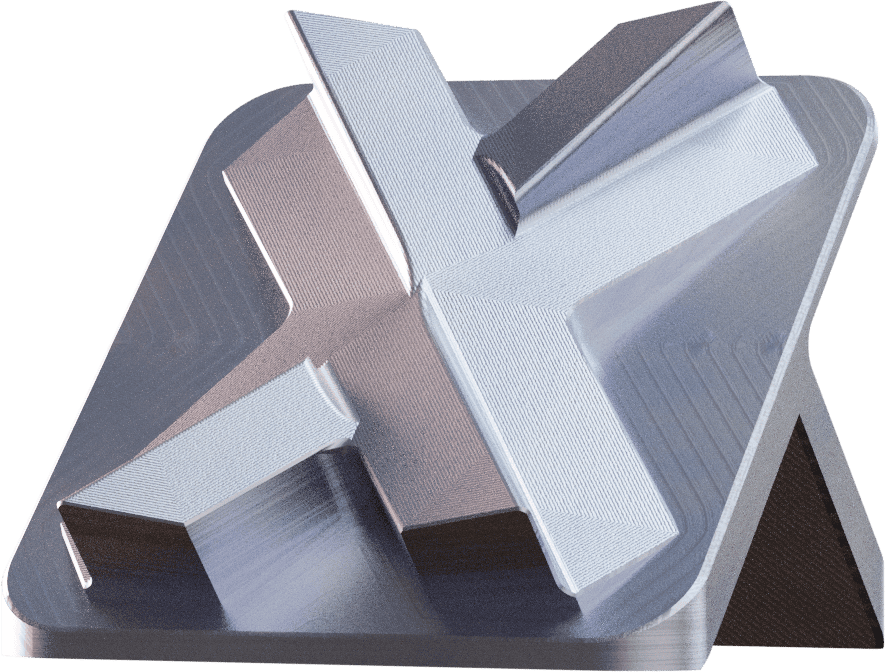
Bead blastedAs machined
Bead blasting
Bead blasting involves spraying a pressurised stream of tiny beads of media, plastic or glass beads, from a nozzle onto the surface of the part. This removes the burrs and imperfections, leaving a smooth finish.
Final result:
- Slightly grainy in the touch
- Uniform, matte or satin-like appearance
-
Electropolishing
An electrochemical process that cleans steel parts to reduce corrosion and improve appearance by making the metal brighter.
Final result:
- Reduced corrosion
- Brighter appearance
-
Media tumbling
Tumbling vibrating media to remove sharp edges and burrs on machined parts.
Notes:Sharp edges may be dulled. Parts with fragile features are not recommended for tumbling.
Final result:
- Smooth in the touch
- Satin-like matte appearance
-
Vapour smoothing
Bathing printed parts in vaporised chemical solvents to create a controlled chemical melt of the material.
Notes:- Can soften sharp edges
- Not suitable for small features and thin walls
Final result:
- Smooth in the touch
- Glossy appearance
-
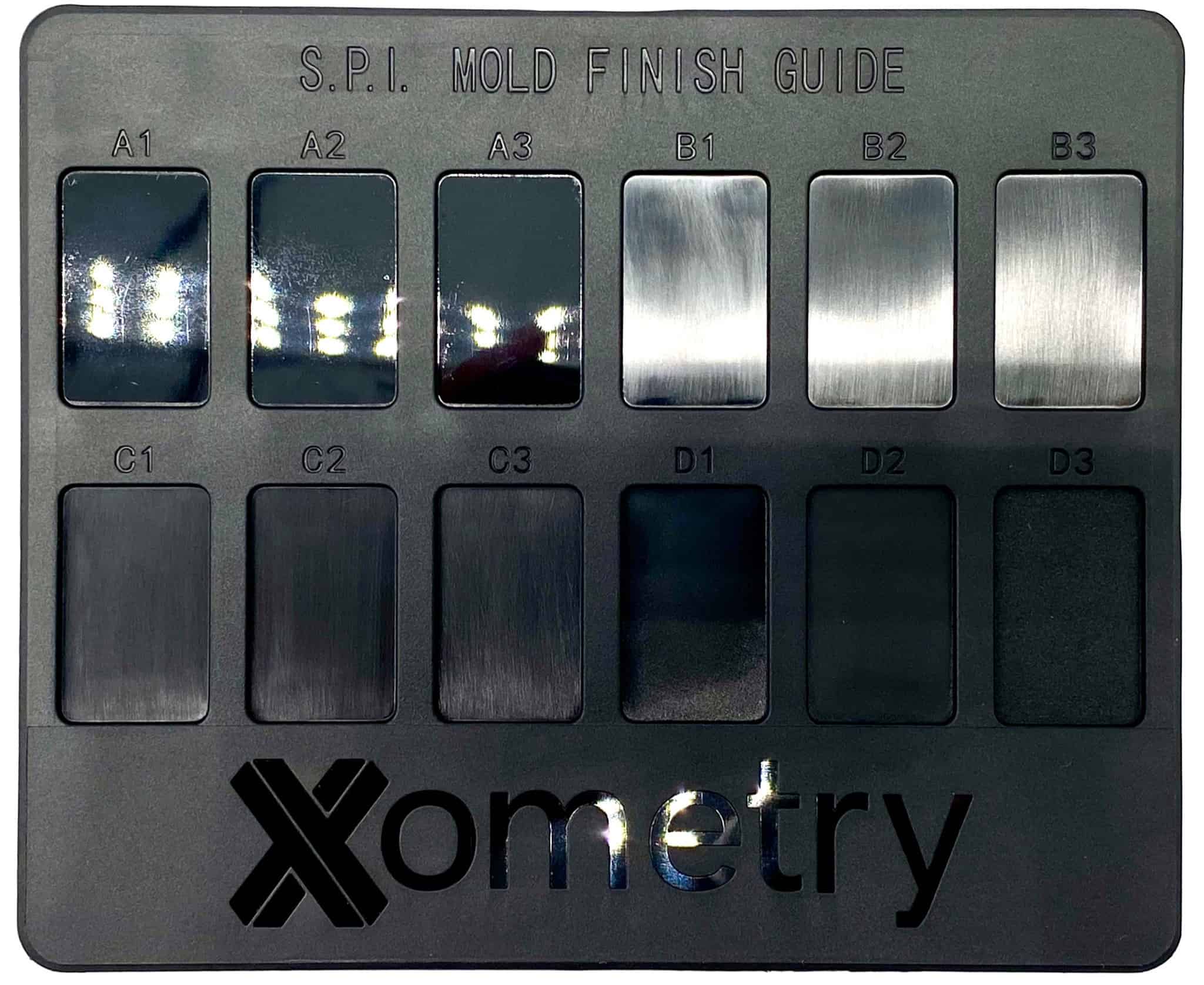
SPI
SPI finishes are a set of standard mould finishes with different polished textures for enhanced properties.
Notes:We recommend providing a CMF (Colour/Material/Finishing) that defines the visual and tactile characteristics of a product, ensuring design consistency and manufacturing accuracy.
Final result:
- Heavily polished, to semi-gloss to fine and coarse matte depending on the selection
- A1, A2, A3, B1, B2, B3, C1, C2, C3, D1, D2, D3
-
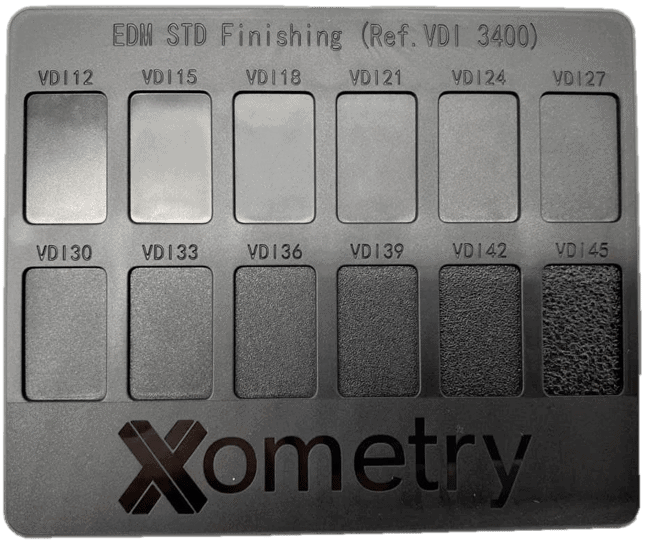
VDI
VDI is an international standard for mould texturing of matte surfaces. It is mainly processed by Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) when mould machining.
Notes:We recommend providing a CMF (Colour/Material/Finishing) that defines the visual and tactile characteristics of a product, ensuring design consistency and manufacturing accuracy.
Final result:
- Fine-to-coarse grain depending on the selection
- VDI12, VDI15, VDI18,VDI21, VDI 24, VDI27, VDI30, VDI33, VDI36, VDI39, VDI42, VDI45
-
Sand blasting
Sand blasting is a surface preparation technique involving high-velocity abrasive particles to remove contaminants and roughen surfaces.
Notes:It’s commonly used for cleaning, texturing, or preparing plastics for processes like painting.
Final result:
- Matte surface
- Enhanced paint adhesion
Adhesives and Coatings
-
Passivation
A colorless coating that improves corrosion resistance for 200 and 300 series and precipitation hardened corrosion-resistant steels by removing free iron from the surface.
-
Quick clear
Clear coat evens out the surface of the part, which allows light to pass through with little distortion.
Final result:
- Enhanced transparency
-
Clear chromate conversion coating / Chem filming (3D render)Gold chromate conversion coating / Chem filming (3D render)
Chromate conversion
Chromate conversion coatings, also known as chem-film, enhance corrosion resistance and conductivity properties and can be used as a base for paint.
Notes:- Type I chromate conversion caused the coating to appear gold or brown in color typically
- Type II chromate coating will appear clear and does not affect surface colouration
Available colors:
- Gold
- Translucent natural
-
Black oxide
Black oxide is a type of conversion coating for ferrous materials, such as steel and stainless steel, which blackens the top layer of the material. It can be used to reduce reflection and glare, as well as provide some additional corrosion resistance without affecting part dimensions.
-
SLS PA 12 dyed, greenSLS PA 12 dyed, yellowSLS PA 12 dyed, black
Dyeing
Colouring parts using dye.
Notes:The dye penetrates 0.25 mm into the part surface.
Available colors:
- Black
- Green
- Yellow
- Red
-
Powder coating
Provides a continuous, protective colour finish on parts using evenly applied, heat-cured paint. The finish is usually tougher and even compared to conventional painting.
Notes:Metals like aluminium and steel can be efficiently coated with polymer powders
Available colors:
- Black
-
MJF PA 12 black spray paintingSLS PA12, black spray painting
Spray painting
Provides a continuous, protective color finish which is applied by spraying.
Notes:- Paint coating is just on the surface level, if it is scratched or subjected to wear and tear, the internal natural colour is visible
- Possibility of requesting custom colours (RAL)
Available colors:
- Black
- Custom colour (RAL)
Anodising
-
Blue anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Gold anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Green anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Orange anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Red anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Yellow anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Anodising, purpleBlack anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)Clear anodising type II (3D render, aluminium shown)
Anodising (type II)
Type II anodise provides increased corrosion resistance and can be used as a base for paint and other finishes.
Notes:- Involves using dyes to affect the part’s surface colour
- Type II coatings are susceptible to wear and may bleach or fade under prolonged direct sunlight
- Possibility of requesting custom colours (RAL)
Available colors:
- Black
- Blue
- Gold
- Green
- Orange
- Red
- Yellow
- Purple
- Grey
- Natural
- Custom colour (RAL)
-
Clear hardcoat anodising type III (3D render, aluminium shown)Grey hardcoat anodising type III (3D render, aluminium shown)Black hardcoat anodising type III (3D render, aluminium shown)PTFE hardcoat anodising type III (3D render, aluminium)
Hardcoat anodising (type III)
Type III hardcoat anodise produces a thicker layer of standard anodising, making it more durable and wear-resistant. Can be used as a base for paint and other finishes.
Notes:Colours tend to come out slightly dark due to the thickness.
Available colors:
- Black
- Grey
- Natural
-
Hardcoat anodising (type III) with PTFE
A hard coat anodise process that embeds PTFE to create a self-lubricating, dry contact surface with Type 3 hard coat’s protective properties.
Notes:This finish can be used on aluminium alloys or titanium and increases the product’s service life.
Final result:
- Colour can vary from light to darker gray or brown
-
Titanium anodising
Titanium anodising is the deliberate electrolytic oxidation of the surface of titanium (or titanium alloy) components to produce surface properties suited to the application for which the part is being made.
Final result:
- Matte gray surface
- Enhanced corrosion and abrasion resistance
Metal & Precious Metal Plating
-
Electroless nickel plating
Electroless nickel plating provides a uniform nickel coating, which offers protection from corrosion, oxidation, and wear on irregular surfaces.
Final result:
- Protection from corrosion, oxidation and wear on irregular surfaces
- Brighter appearance
-
Gold plating
Gold Plating provides good corrosion and tarnish resistance. Gold has low contact resistance, excellent conductivity, and solderability.
Final result:
- Gold-like appearance
- Increased corrosion and tarnish resistance
-
Silver plating
Electroplating silver provides good corrosion resistance but easily tarnishes. Silver offers high solderability and electrical conductivity.
Final result:
- Silver-like appearance
- Increased corrosion-resistance
- Easily tarnishes
-
Zinc coating / Galvanising
Zinc plating involves the electrodeposition of a thin coating of zinc metal onto the surface of another metal object, known as a substrate.
Notes:The zinc coating creates a physical barrier that prevents rust from reaching the underlying metal surface.
Final result:
- Increased corrosion resistance
Heat Treatments
-
Annealing
The annealing process involves the heating of a metal to or near the temperature at which recrystallisation begins without change in the stresses. After heating, the metal is cooled to room temperature in the oven or put in the sand.
Final result:
- Improved cold working capacity of the metal
-
Case-hardening (Carburising)
A heat treatment process which includes hardening the surface of metal while allowing the metal underneath to remain soft. As the name implies, carburising is inducting carbon or nitrogen into low-carbon alloys at elevated temperatures so that the hardenability increases.
-
Tempering
A heat treatment method that is mainly dedicated to reducing the amount of hardness of metals. It involves heating the metal to a temperature below the critical point. The temperature is adjusted depending on the amount of hardness that needs to be reduced and it varies depending on the metal type as well.
Final result:
- Reduced hardness
- Increased elasticity and plasticity
- Reduced yield and tensile strength
-
Through hardening
Through hardening, also known as quench hardening, is a heat treatment process used to increase the hardness and strength of a material by heating it to a high temperature and then rapidly cooling it, usually by immersing it in a quenching medium such as oil, water, or air.
Final result:
- Hardened surface layer that is resistant to wear, abrasion, and deformation
- The core remains tough and ductile
Choose From 40+ Finishing Options for Your Parts
Upload Your CAD Files Or Update Your QuoteAll uploads are secure and confidential.
 Europe
Europe  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Türkiye
Türkiye  USA & Canada
USA & Canada  Asia
Asia