Fused deposition modeling (FDM) is an extrusion-based 3D printing technology. The build materials used in FDM are thermoplastic polymers and come in a filament form. In FDM, a part is manufactured by selectively depositing melted material layer by layer in a path defined by the CAD model. Due to its high accuracy, low cost and large material selection, FDM is one of the most widely used 3D printing technologies across the world.
How Does Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Work?
FDM technology uses the build input material in the form of thermoplastic filaments which is liquified and re-solidified into the desired shape according to the defined CAD model.
An FDM printer consists of two spools: one for the build material and the other for the support material respectively. The Fused deposition modeling 3D printing process follows these main steps:
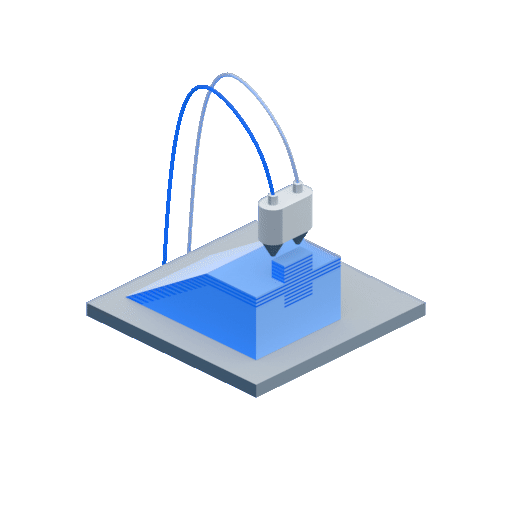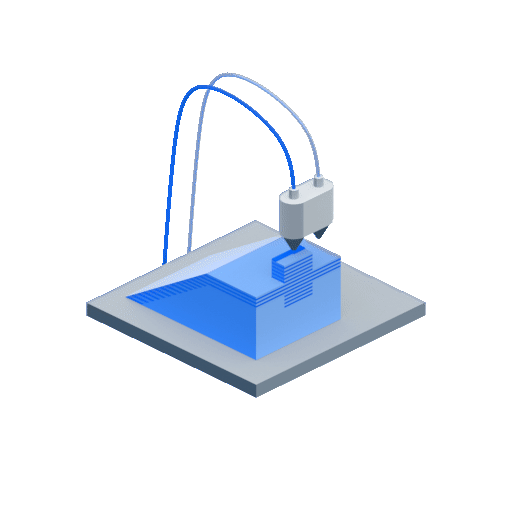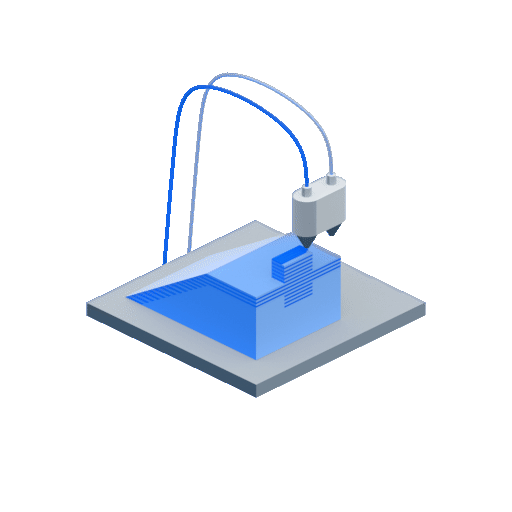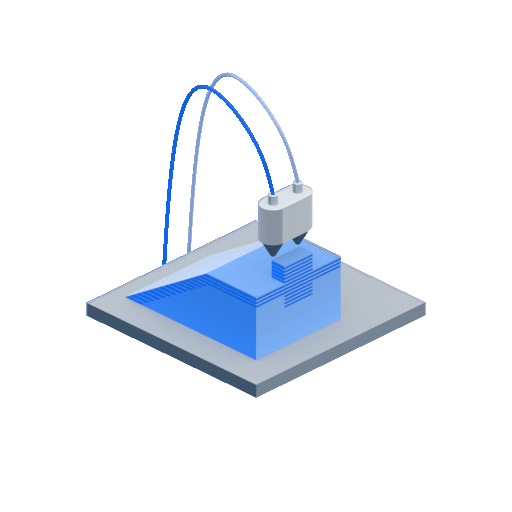
- Step 1 – After the CAD data is input, the already loaded solid build material filament is liquified with the help of heat in the liquefier head
- Step 2 – This molten liquid plastic is fed onto the foam build platform as a layer through the extrusion nozzle that moves in all directions as defined in the CAD data. This process of adding the liquid/semi-solid layers one above the other is repeated. If the design consists of over-hangs or structures that might potentially warp or bend, support structures are used. The support material can be the same as the build material or any other material according to the choice.
- Step 3 – In case support structures were used, they are later removed once the build is complete.
Materials for FDM 3D Printing
Amongst the most widely rigid plastics used for fused deposition modeling, Xometry offers: ABS, ABS ESD7, ABS M30, ASA, Nylon PA12, Nylon PA12 Carbon-Filled, Carbon Fiber Reinforced Polyamide 12, PC-ABS Polycarbonate, PC-ISO Polycarbonate, PC-like Heat Resist Translucent, PC-Polycarbonate, PLA, PETG, PEEK, ULTEM 1010, and ULTEM 9085.
ASA, an amorphous thermoplastic with improved weather resistance, is widely used in prototyping thanks to its excellent mechanical properties. Plus, it is available in a large variety of colours.
Advantages of FDM Technology
When coming to the FDM process, these are the most important factors that make it one of the most popular 3D printing technologies.
Cost-Effectiveness
FDM is known as one of the cheapest options for 3D printing. When the requirement is from a unit to a small batch, FDM is the ideal option compared to its more expensive counterparts like SLA or SLS. Moreover, the build material is cheaper and widely available, which makes the prototyping, re-prototyping and improvements in design less expensive to print than with other technologies.
Colouring and surface finish costs are also reduced as the prints come out coloured with decent surface finish directly from the printer without the fuss of additional post-processing.
Quick Turnaround
The FDM process is quick in terms of printing speeds, faster than many other technologies. Since the build filaments are easily available, there is no problem with time in printing big batches too. Xometry delivers FDM printed parts in as fast as 3 business days.
Can Print in Full-Colour
More than 40 colours are available for FDM printers, and the number of colour options keeps increasing day by day. The colour of the final part is exactly the colour of the filament used. If the desired colour is not obtained, post-processing methods like dying or painting are also available.
Less Material Wastage
Since the FDM printer prints by melting the filament and solidifying it, there is no chance of wastage involved like in MJF or SLS where the powder is used and prone to wastage. There is also a chance of eliminating the support structures when the model is designed carefully.
Wide Variety of Materials
Over 10 different varieties of plastic filaments are available for FDM. From low strength to high strength materials (PP, TPU, Nylon PA, ABS, PETG, PLA, PC in the ascending order of tensile strength), FDM has an extensive list of materials with which it can print. It is the manufacturer’s discretion on what to use depending on the need. One other advantage is the material availability. The materials are very often used and hence easily available in the market for a low price.
Disadvantages of FDM Process
Apart from the advantages it offers, there are also a few common disadvantages that FDM possesses.
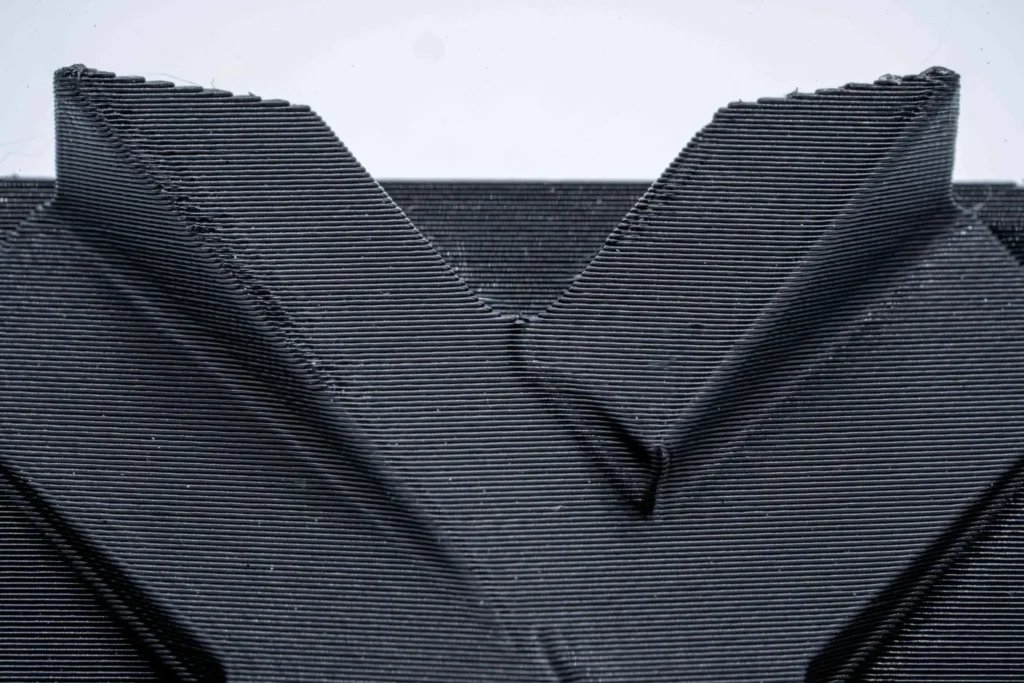
Significant Layer Stepping
The surface quality of FDM printed parts is not smooth like resin printed parts of SLA or Carbon DLS. Since FDM works by dropping molten plastic layer by layer, the stair casing or layer stepping is much more evident. The image shows a rough surface due to the staircase effect. Moreover, the layer adhesion mechanism makes FDM parts anisotropic. Post-processing is required to make the surface smooth and costs more.

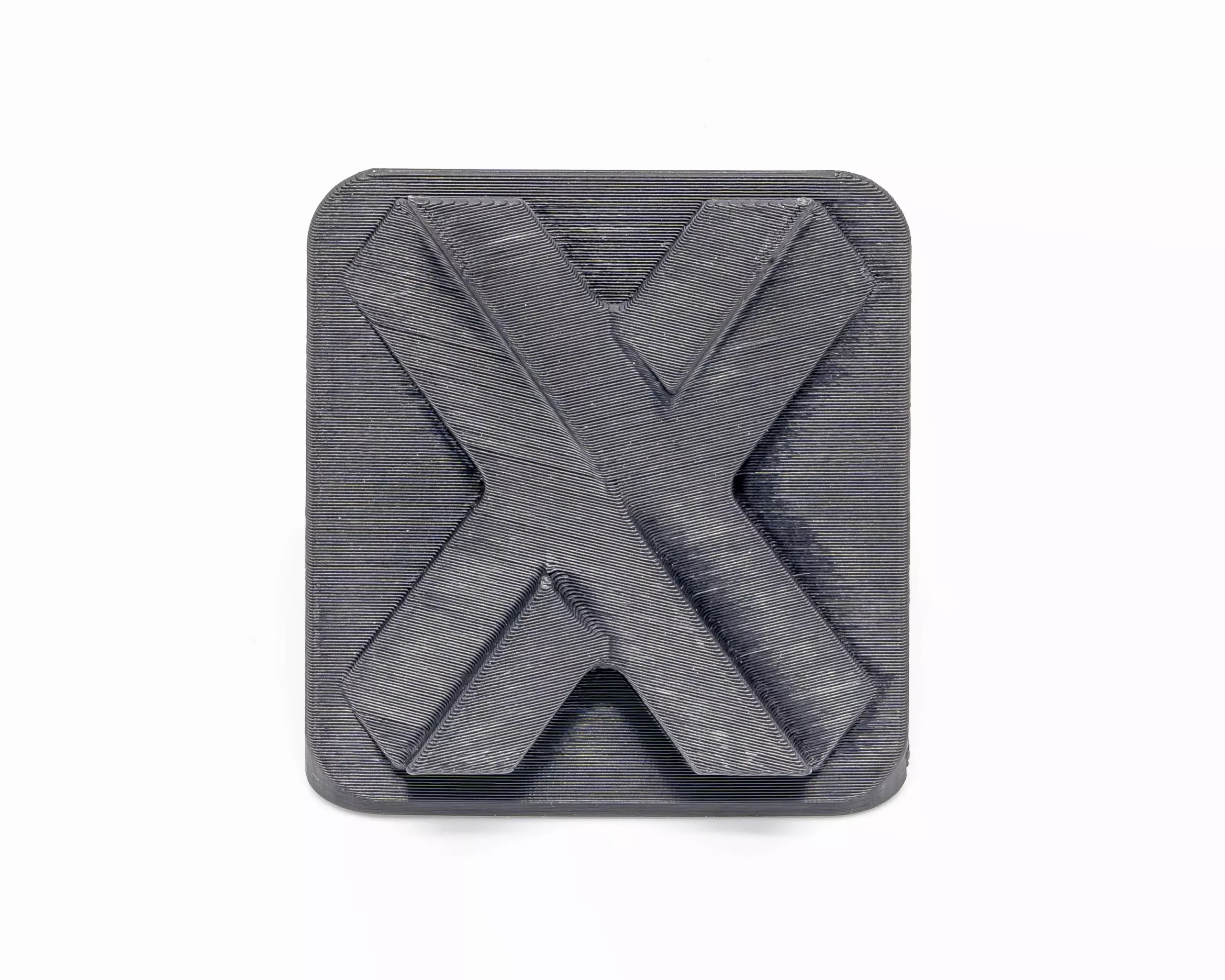
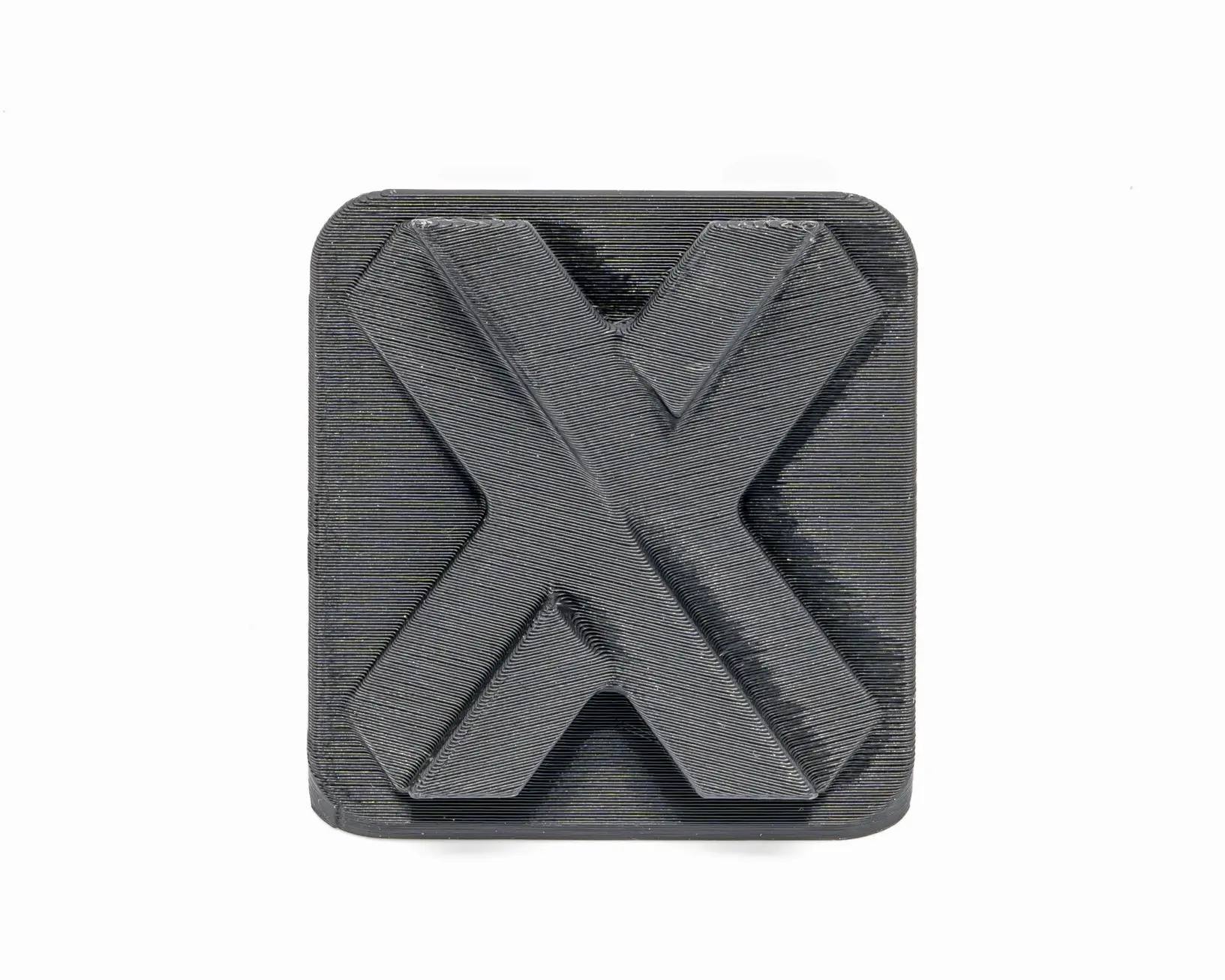
Sweats Small Details
Due to the nature of melted plastic, FDM sweats small features and has the lowest dimensional accuracy and resolution compared to other 3D printing technologies and hence it is not suitable for parts with intricate details. FDM is surely a good option for prototyping where small details are not important. If details and dimensional accuracy are a concern, it’s better to avoid FDM.
Xometry’s FDM 3D Printing Services
Xometry Europe offers Fused deposition modeling services online, for on-demand 3D printing projects, for both prototypes and large batches. With a network of more than 2,000 partners all over Europe, Xometry is able to deliver FDM 3D printing parts in up to 3 days. Upload your CAD files to Xometry Instant Quoting Engine to get an instant quote with various manufacturing options available for FDM 3D printing.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0






 Download
Download