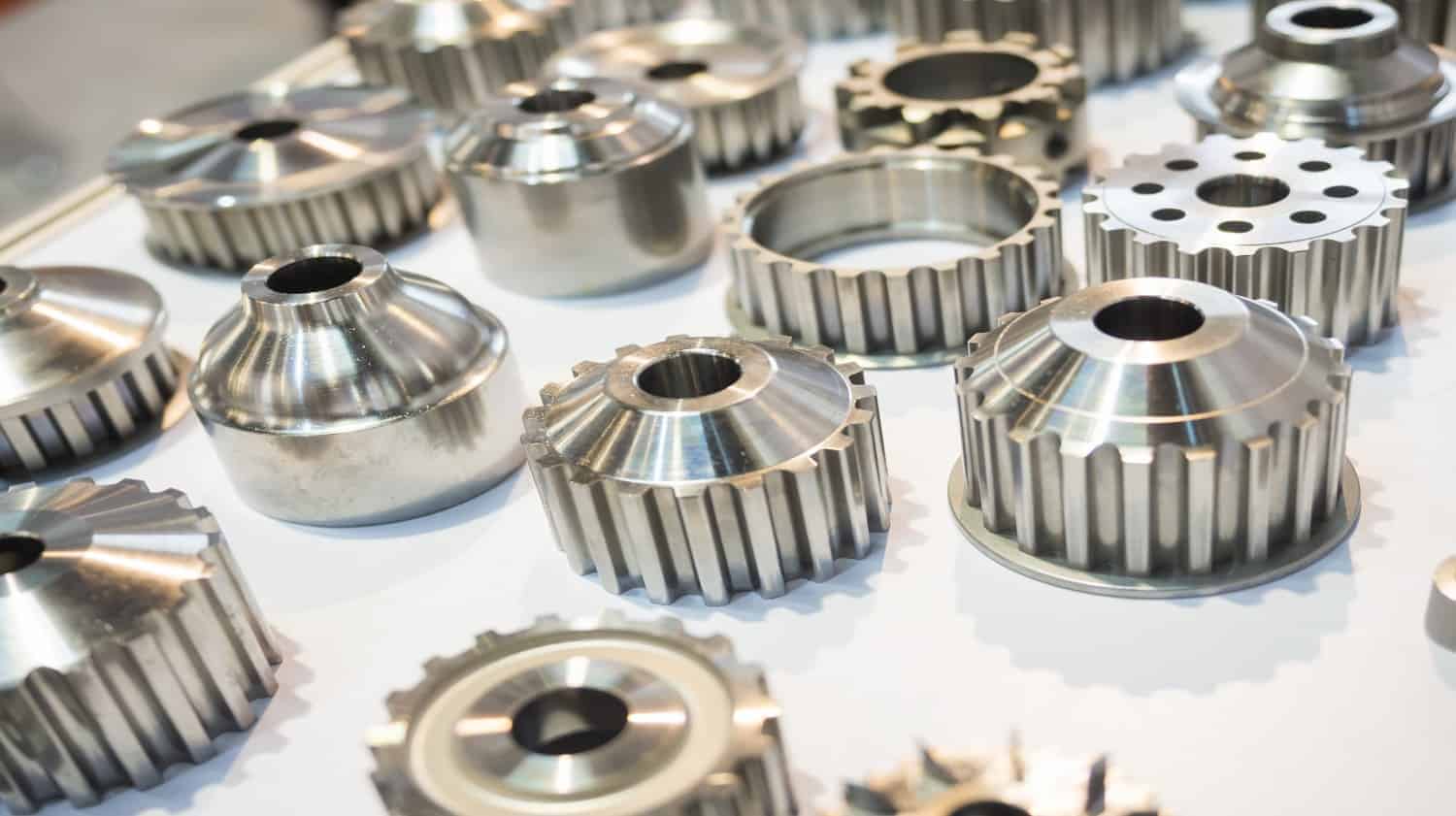
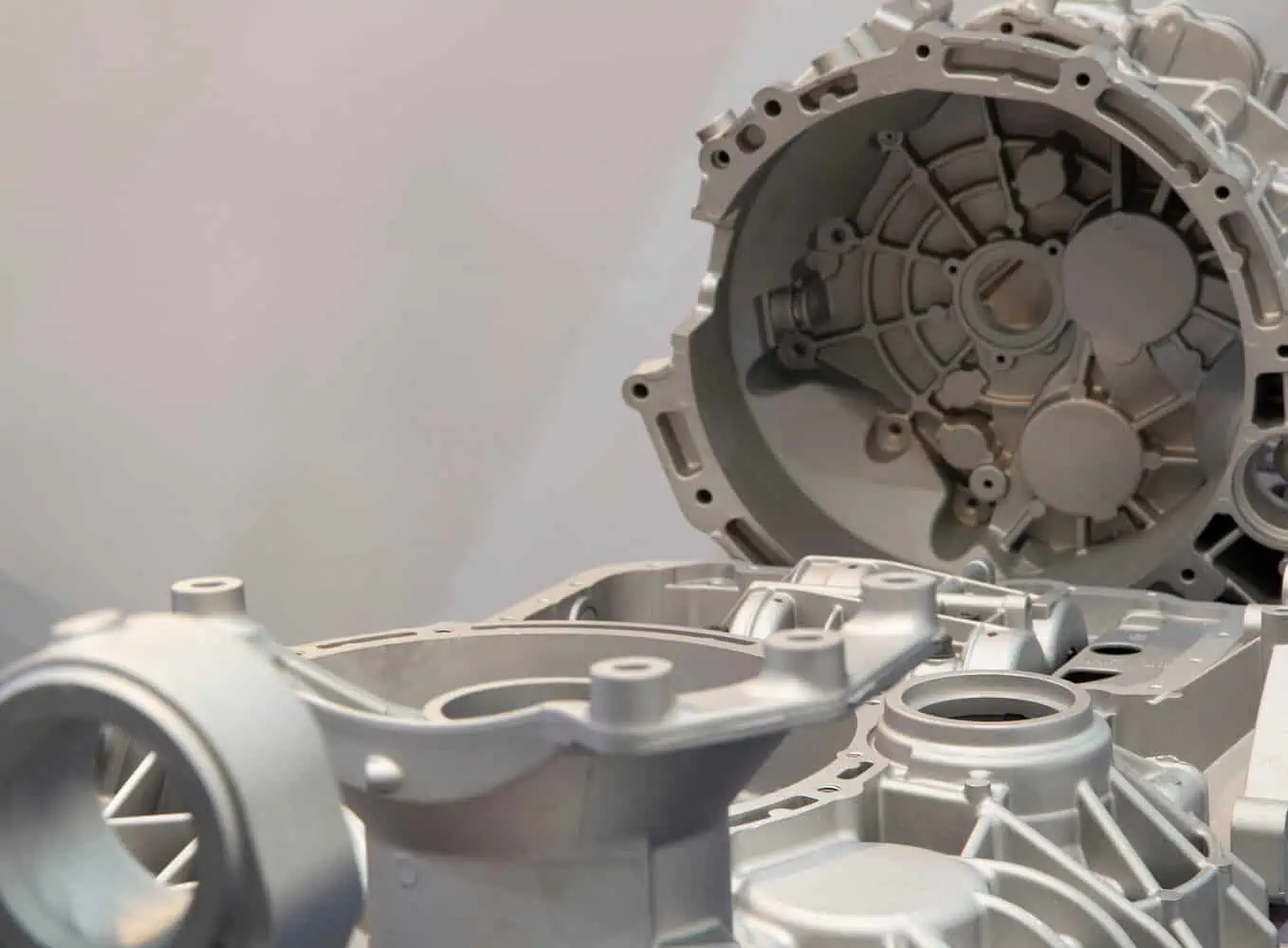
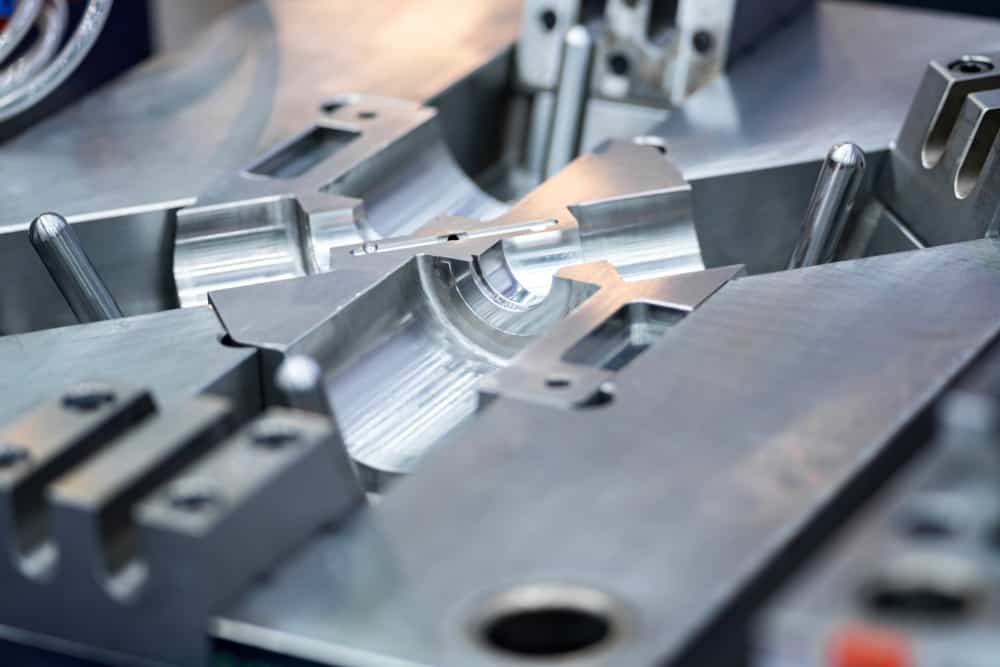
Die casting is a metal casting process often used to create high-quality, durable parts for use in various applications. Die casting may be the perfect choice for your business if you’re looking for a manufacturing process that can produce top-quality metal parts.
What is Die Casting?
Die casting is a manufacturing process that allows the production of metal parts with a high degree of precision. In this casting process, molten metal is injected into a mould, where it cools and hardens to create the desired shape.
The method can be used to create various metal parts, from gears and engine blocks to door handles and electrical components.
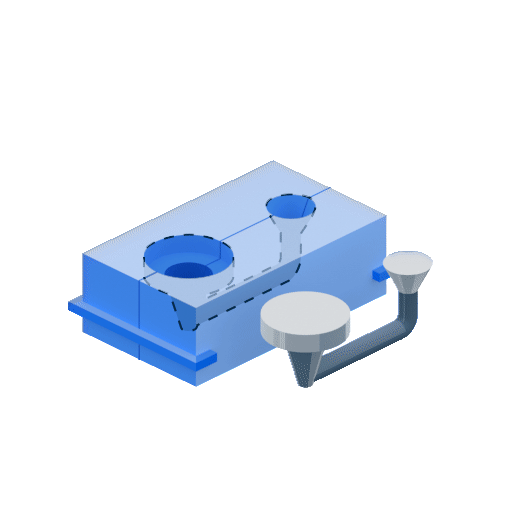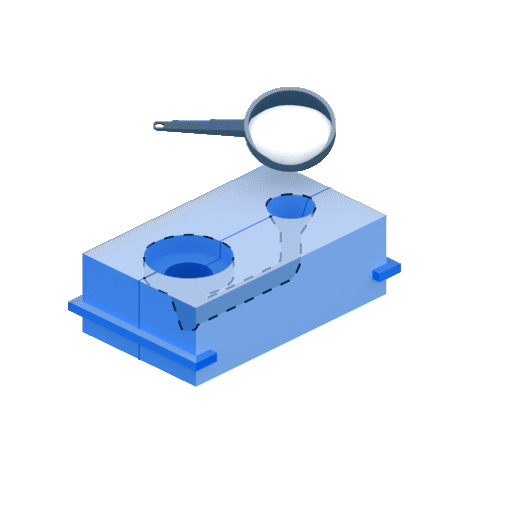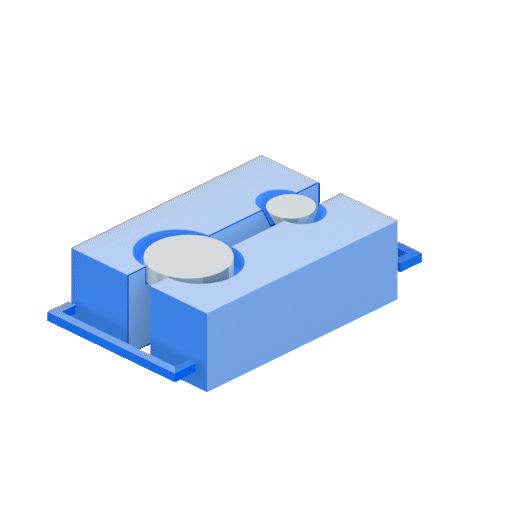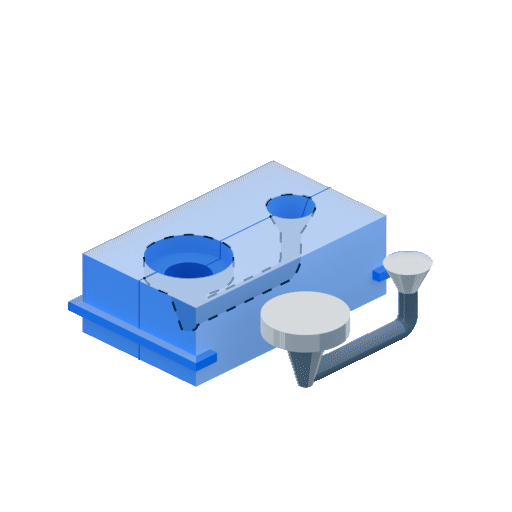
Die casting is prized for its ability to produce parts with a smooth surface finish and precise dimensions. In addition, this process is relatively fast and cost-effective, making it an attractive option for many applications.
How Does Die Casting Work?
The die casting process involves several steps, including mould design, metal preparation, injection, casting, and finishing.
Step 1 – Mould Design
The initial step in the die casting process is creating a mould called a die. This mould is usually made from steel or aluminium and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the die casting process.
The mould design begins with developing a CAD design of the required mould. This design is then used to create a mould by CNC machining, which is further used in the casting process.
Step 2 – Metal Preparation
The next step is to prepare the metal for injection. This metal is typically an alloy, such as aluminium, magnesium, or zinc. The metal is melted in a furnace and then poured into a ladle.
Step 3 – Injection Process
Once the metal is in a liquid state, it is injected into the mould under high pressure. The molten metal fills the mould cavity and cools to create the desired shape.
Step 4 – Casting Process
After the metal has cooled and hardened, the mould is opened, and the part is ejected. Ensure that the part has cooled entirely before handling to avoid any potential injuries.
Step 5 – Finishing Process
The final step in the process is to finish the part. Surface finishing plays a vital role in die casting, as it can impact the durability and function of the part. Standard finishing processes include anodizing, powder coating, wet plating, and many more.
Types of Die Casting
There are several different types of die casting, each of which has unique benefits. The two most common types of die casting are cold chamber and hot chamber.

Cold Chamber Die Casting
In this type of die casting, the molten metal is injected into the mould cavity using a cold-chamber machine. This machine is typically used to cast metals with high melting points, such as aluminium. The main advantage of cold chamber die casting is that it can be used with various metals and reduces machine corrosion.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Hot chamber die casting is the most popular method and is relatively faster than cold chamber die casting. A hot-chamber machine is used to perform this process in hot chamber die casting. This machine generally uses metals with a lower melting point, such as zinc.
Both hot chamber and cold chamber die casting offer high accuracy and precision. In addition, both processes are relatively fast and cost-effective.
Suitable Die Casting Materials
When you are ready to begin your die-casting project, one of the most important decisions you will make is choosing the suitable material. The material you select must be able to withstand the high temperatures and pressures of the die casting process, as well as the demands of your end-use application.
Furthermore, it is important to choose a material that is compatible with the die casting operation you have selected. With so many factors to consider, working with an experienced die-casting partner who can help you navigate the many options and make the best decision for your specific project is essential.
However, aluminium, magnesium, and zinc are three of the most popular die casting materials, as they all are strong and lightweight:
Aluminium Alloys
Aluminium is also highly corrosion-resistant, making it an ideal choice for die-cast parts that will be exposed to the elements. Some of its most suitable aluminium alloys for die casting are:
- Aluminium 46100 / ADC12 / A383 / Al-Si11Cu3
- Aluminium 46500 / A380 / Al-Si8Cu3
Magnesium Alloys
Magnesium alloys such as AZ91D, AM60B, and AS41B are also well suited for die casting due to their high strength-to-weight ratio. In addition, these alloys offer good resistance to corrosion and wear.
Zinc Alloys
Zinc, on the other hand, is an excellent conductor of heat and electricity, making it ideal for die-cast parts that will need to be heated or cooled rapidly.
Advantages of Die Casting
When it comes to mass-producing metal parts, die casting is one of the most efficient and cost-effective methods. It’s a process that has been around for centuries, but its popularity has grown in recent years as manufacturers seek ways to reduce production costs.
Here are some of the advantages of die casting:
- Complex shapes: Die casting is a process that can produce complex shapes with tight tolerances
- Versatility: The process is versatile and can be used to cast a variety of metals, including aluminium, zinc, and magnesium
- High production rate: It is a relatively fast process, which can be an advantage when time is of the essence
- Cost-efficient: The process is also relatively inexpensive, making it a cost-effective option for many applications
- Repeatability: It also allows for a high degree of repeatability, meaning that parts can be manufactured to precise specifications.
Applications of Die Casting
Die casting is used in a variety of industries and applications. Some of the most common uses for die casting include:
- Automotive industry: Die casting is used extensively in the automotive industry. It’s often used to create engine blocks, cylinder heads, and transmission cases
- Electrical industry: The electrical industry also relies on die casting for a variety of applications. Die-cast parts are used in the manufacture of electrical components such as switchgear, panel boards, and circuit breakers
- Aerospace Industry: The aerospace industry is a major user of die casting. The manufactured parts are used in the manufacture of aircraft and spacecraft components
- Appliance Industry: The appliance also uses this process to manufacture die-casted parts for many appliances
- Furniture Industry: It is also used in the furniture industry. It’s often used to create furniture hardware such as drawer pulls and knobs
Many other industries use die-casting processes for medical, construction, and toy industries. It is a versatile process that can be used to create various parts and products.

Get Started With Die Casting
Die casting is a manufacturing process that has been around for centuries and continues to be popular because of its versatility and ability to create complex shapes. The process can be used to create metal parts for a variety of industries, including automotive, aerospace, furniture, and appliance manufacturing.
Through our extensive network of manufacturers, Xometry Europe offers die casting services for several dozens of materials including aluminium, magnesium and zinc alloys. Simply head over to our Instant Quoting Engine to upload your model and receive a quote to order parts.
 Europe
Europe  Türkiye
Türkiye  United Kingdom
United Kingdom  Global
Global 

 Login with my Xometry account
Login with my Xometry account  0
0





